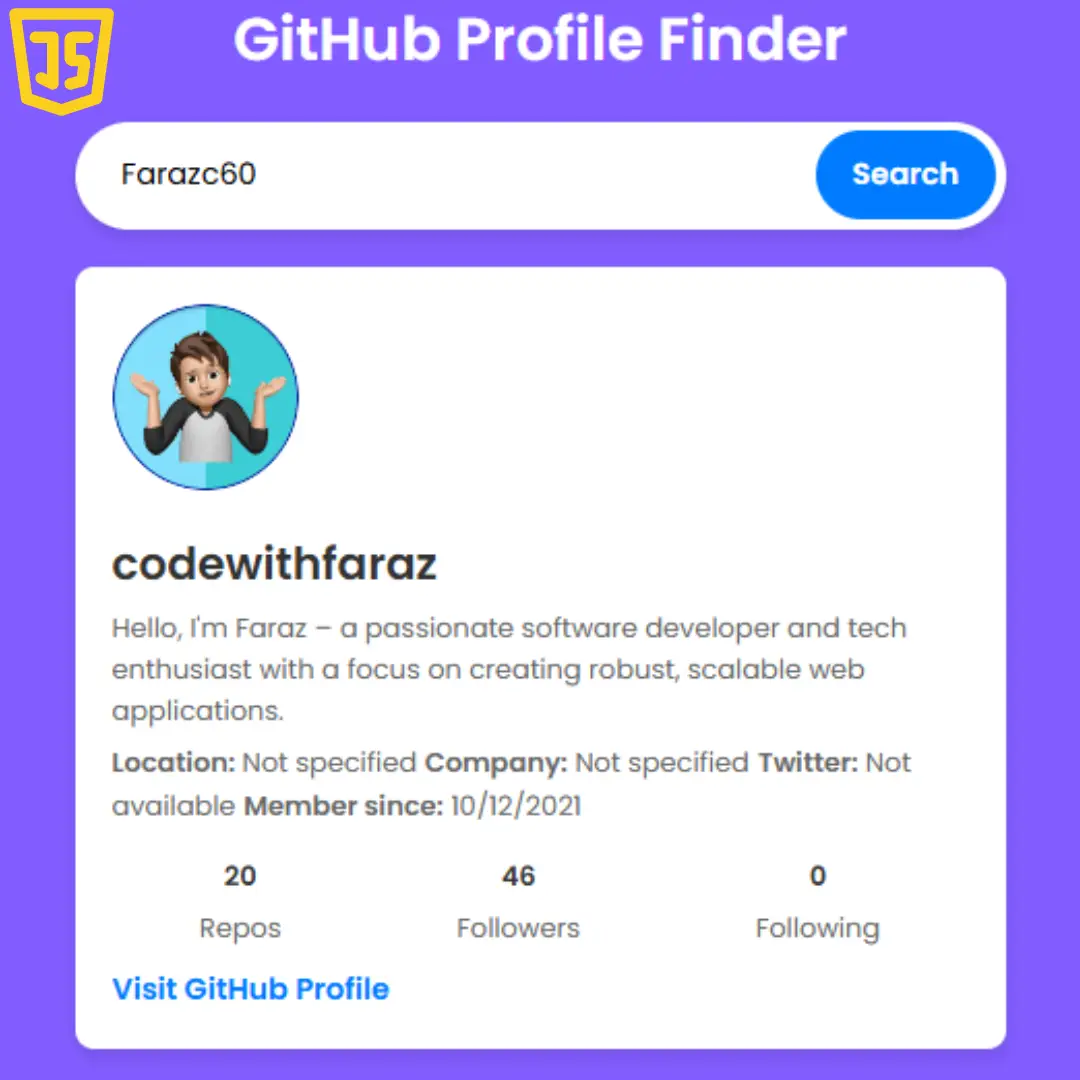
In this tutorial, we will show you how to create a pure CSS animated search box using HTML and CSS.

Table of Contents
When designing a website, it is important to pay attention to even the smallest details, such as the search box. The search bar is one of the most important elements of a website. It is used to connect people to websites. It acts as a field for the user's query input or search term to search and retrieve related data from the database. In this tutorial, we will be creating a pure CSS animated search box using HTML and CSS.
Pure CSS is a technique that involves using only CSS to create designs, without the need for JavaScript. This tutorial will show you how to create a beautiful animated search box using only HTML and CSS, with no external libraries or frameworks.
Let's start making an amazing animated search box using HTML and Pure CSS step by step.Join My Telegram Channel to Download the Project: Click Here
Prerequisites:
Before starting this tutorial, you should have a basic understanding of HTML and CSS. Additionally, you will need a code editor such as Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text to write and save your code.
Source Code
Step 1 (HTML Code):
The first step in creating a pure CSS animated search box is to create a basic HTML file and write the HTML markup. We will be using semantic HTML, which means using HTML elements that describe the content they contain. This makes it easier for search engines and screen readers to understand the content of the website.
To create the search box, we will use a form element, with an input element for the search bar and a button element for the search button.
After creating the files just paste the following codes into your file. Make sure to save your HTML document with a .html extension to properly view it in a web browser.
This is the basic structure of our animated search box using HTML, and now we can move on to styling it using CSS.
Step 2 (CSS Code):
After creating the HTML markup, we will now style the search box using CSS. We will first set the box-sizing to border-box, which means that the padding and border of an element will be included in the total width and height of the element.
Here's a breakdown of the key parts of the code:
Global Styles
* {
border: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}- Resets the margins, paddings, and borders for all elements. It also sets the
box-sizingtoborder-box, meaning padding and border will be included in the element's total width and height.
Root Font Size (Responsive)
:root {
font-size: calc(16px + (24 - 16)*(100vw - 320px)/(1920 - 320));
}- Dynamically adjusts the root font size based on the viewport width (
vw). The font size scales between 16px and 24px, depending on the screen width, from 320px (mobile) to 1920px (desktop).
Body and Inputs
body, button, input {
font: 1em Hind, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.5em;
}
body, input {
color: #171717;
}- Sets the font and line height for
body,button, andinput. All text will be styled in the "Hind" font and will have a color of#171717(a dark gray).
Body Styling
body, .search-bar {
display: flex;
}
body {
background: #755e88;
height: 100vh;
}- The
bodyand.search-barelements usedisplay: flexfor flexible layout. The body has a background color#755e88and takes up the full viewport height (100vh).
Search Bar Transitions
.search-bar input, .search-btn, .search-btn:before, .search-btn:after {
transition: all 0.25s ease-out;
}- Applies a smooth transition for 0.25 seconds to the search input, button, and pseudo-elements (
:beforeand:after) for any property change.
Search Bar Layout
.search-bar input, .search-btn {
width: 3em;
height: 3em;
}- Sets a fixed width and height of
3emfor the search input and button.
Input Focus and Invalid State
.search-bar input:invalid:not(:focus), .search-btn {
cursor: pointer;
}- When the input is invalid and not focused, and for the button, the cursor changes to a pointer.
Search Bar Focus and Valid Styles
.search-bar input:focus, .search-bar input:valid {
background: #fff;
border-radius: 0.375em 0 0 0.375em;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.1em #d9d9d9 inset;
transform: scale(1);
}- When the input is focused or valid, the background becomes white, the corners round slightly (
border-radius), and a shadow is added. The input is also scaled back to its original size.
Search Button Styling
.search-btn {
background: #171717;
border-radius: 0 0.75em 0.75em 0;
transform: translate(0.25em, 0.25em) rotate(45deg) scale(0.25, 0.125);
}- Styles the search button as a black button (
#171717) with a rounded right side. It also applies a rotated and scaled transformation to the button.
Pseudo-elements for the Search Button
.search-btn:before, .search-btn:after {
content: "";
display: block;
opacity: 0;
position: absolute;
}- The
:beforeand:afterpseudo-elements are used to visually represent parts of the search button, but they are initially hidden (opacity: 0).
Search Button Appearance on Focus
.search-bar input:focus + .search-btn, .search-bar input:valid + .search-btn {
background: #2762f3;
transform: scale(1);
}
.search-bar input:focus + .search-btn:before, .search-bar input:valid + .search-btn:before {
opacity: 1;
}- When the input is focused or valid, the button changes its background to blue (
#2762f3) and its transform scales back to its original size. The pseudo-elements (:before,:after) also become visible (opacity: 1).
Dark Mode
@media screen and (prefers-color-scheme: dark) {
body, input {
color: #f1f1f1;
}
body {
background: #171717;
}
}- If the user prefers dark mode, the colors of the body and inputs are inverted: the text becomes light (
#f1f1f1), and the background becomes dark (#171717).
This will give our search box an upgraded presentation. Create a CSS file with the name of styles.css and paste the given codes into your CSS file. Remember that you must create a file with the .css extension.
* {
border: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
:root {
font-size: calc(16px + (24 - 16)*(100vw - 320px)/(1920 - 320));
}
body, button, input {
font: 1em Hind, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.5em;
}
body, input {
color: #171717;
}
body, .search-bar {
display: flex;
}
body {
background: #755e88;
height: 100vh;
}
.search-bar input,
.search-btn,
.search-btn:before,
.search-btn:after {
transition: all 0.25s ease-out;
}
.search-bar input,
.search-btn {
width: 3em;
height: 3em;
}
.search-bar input:invalid:not(:focus),
.search-btn {
cursor: pointer;
}
.search-bar,
.search-bar input:focus,
.search-bar input:valid {
width: 100%;
}
.search-bar input:focus,
.search-bar input:not(:focus) + .search-btn:focus {
outline: transparent;
}
.search-bar {
margin: auto;
padding: 1.5em;
justify-content: center;
max-width: 30em;
}
.search-bar input {
background: transparent;
border-radius: 1.5em;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.4em #171717 inset;
padding: 0.75em;
transform: translate(0.5em,0.5em) scale(0.5);
transform-origin: 100% 0;
-webkit-appearance: none;
-moz-appearance: none;
appearance: none;
}
.search-bar input::-webkit-search-decoration {
-webkit-appearance: none;
}
.search-bar input:focus,
.search-bar input:valid {
background: #fff;
border-radius: 0.375em 0 0 0.375em;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.1em #d9d9d9 inset;
transform: scale(1);
}
.search-btn {
background: #171717;
border-radius: 0 0.75em 0.75em 0 / 0 1.5em 1.5em 0;
padding: 0.75em;
position: relative;
transform: translate(0.25em,0.25em) rotate(45deg) scale(0.25,0.125);
transform-origin: 0 50%;
}
.search-btn:before,
.search-btn:after {
content: "";
display: block;
opacity: 0;
position: absolute;
}
.search-btn:before {
border-radius: 50%;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.2em #f1f1f1 inset;
top: 0.75em;
left: 0.75em;
width: 1.2em;
height: 1.2em;
}
.search-btn:after {
background: #f1f1f1;
border-radius: 0 0.25em 0.25em 0;
top: 51%;
left: 51%;
width: 0.75em;
height: 0.25em;
transform: translate(0.2em,0) rotate(45deg);
transform-origin: 0 50%;
}
.search-btn span {
display: inline-block;
overflow: hidden;
width: 1px;
height: 1px;
}
.search-bar input:focus + .search-btn,
.search-bar input:valid + .search-btn {
background: #2762f3;
border-radius: 0 0.375em 0.375em 0;
transform: scale(1);
}
.search-bar input:focus + .search-btn:before,
.search-bar input:focus + .search-btn:after,
.search-bar input:valid + .search-btn:before,
.search-bar input:valid + .search-btn:after {
opacity: 1;
}
.search-bar input:focus + .search-btn:hover,
.search-bar input:valid + .search-btn:hover,
.search-bar input:valid:not(:focus) + .search-btn:focus {
background: #0c48db;
}
.search-bar input:focus + .search-btn:active,
.search-bar input:valid + .search-btn:active {
transform: translateY(1px);
}
@media screen and (prefers-color-scheme: dark) {
body, input {
color: #f1f1f1;
}
body {
background: #171717;
}
.search-bar input {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.4em #f1f1f1 inset;
}
.search-bar input:focus,
.search-bar input:valid {
background: #3d3d3d;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.1em #3d3d3d inset;
}
.search-btn {
background: #f1f1f1;
}
} Final Output:

Conclusion:
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to create a pure CSS animated search box using HTML and CSS. We covered the HTML markup, CSS styling, and adding animation to the search box. A well-designed search box can improve the user experience and overall aesthetic of a website. We hope this tutorial has been helpful and inspires you to create your own beautiful search box using pure CSS.
That’s a wrap!
I hope you enjoyed this post. Now, with these examples, you can create your own amazing page.
Did you like it? Let me know in the comments below 🔥 and you can support me by buying me a coffee
And don’t forget to sign up to our email newsletter so you can get useful content like this sent right to your inbox!
Thanks!
Faraz 😊